Random Variables
Lecture 6
NC State University
ST 511 - Fall 2024
2024-09-09
Checklist
– Have you turned in HW-1
- Late window is by tonight at 11:59pm
- Grades have a ~ 1 week turn around– HW-2 released Monday (9-16)
– Quiz 3 released this Wednesday
Why did we spend time on data visualization?
– Every good data analysis starts with a good data exploration
– Effective data visualization when communicating to a larger audience
Why did we spend time on data visualization?
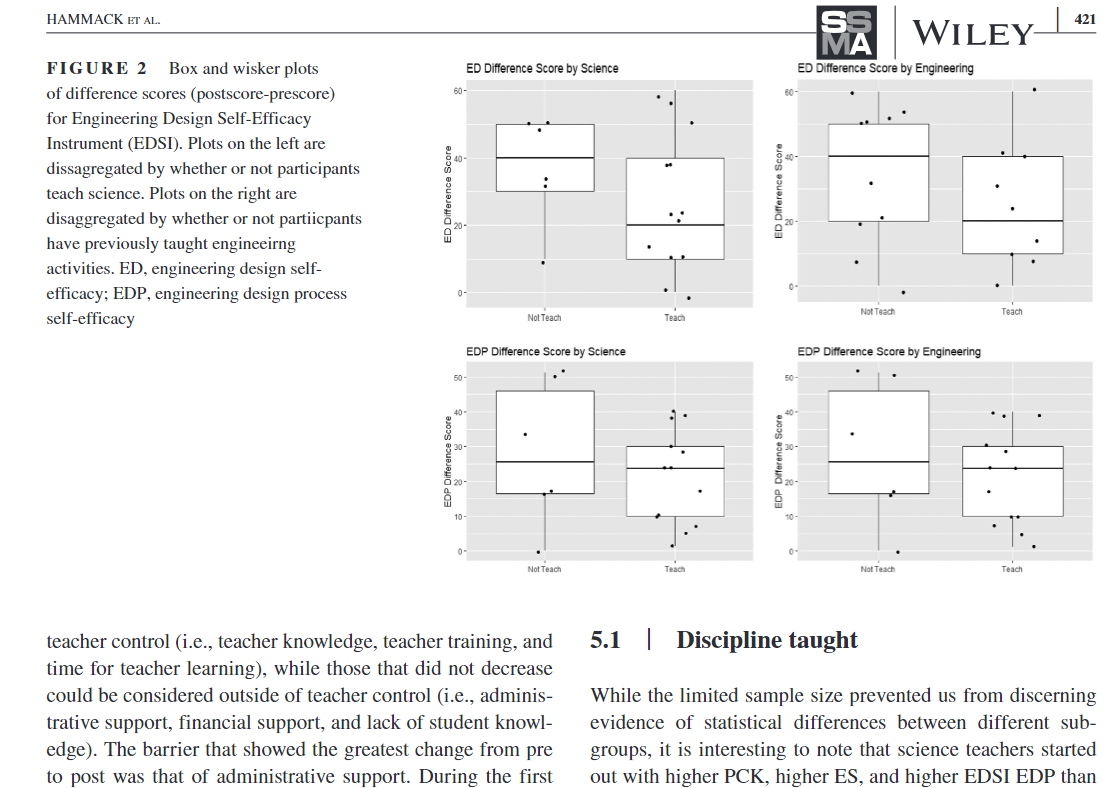
Impacts of professional development focused on teaching engineering applications of mathematics and science
Inference
Terms
– Population - The complete set of observational units you are collecting data on
Examples
– All NC State Students
– All fish in the Missouri river
– All trees in Umstead State Park
Example
What is the mean height of of all NC State students?
How confident are you in your guess?
Terms
Sample - A subset of observational units you are collecting data on
Example
What is the mean height of of all NC State students?
Suppose I asked 50 students their height before class and found the following:
\[ \bar{x} = 5ft - 6 inches \] Are you confident in this guess?
Do you think this guess is correct?
If we took another sample, do you think we would get the same answer?
The Big Picture
– Want to make a claim about a population
– But we can’t, because variability exists
– We need a way to quantify variability so we can make claims about the population we are interested in
The process
Knowing the following concepts lays the foundation for us to perform inference
– Random Variables
– Probability distributions
– Sampling distributions
Random Variables
Ways to map random process to numbers
What do we mean by a random process?
Random Variables
\[ X = \begin{cases} 1 & \text{if heads}\\ 0 & \text{if tails} \end{cases} \]
Random Variables
\[ Y =\text{sum of two rolled dice}\\ \]
Why do we care?
Why do we care?
– A random variable can take on many many values
– Defining random variables (maps a random process to values) helps us calculate probabilities
– Calculating probabilities is fundamental in statistical inference